Cybersecurity: The Basic Principles & Tools for Risk Management

The recent statistics of crimes associated with information technologies keeps dramatically growing. According to experts’ estimation, about 145 billion email messages run over the globe daily. Among them, 65% are spamming while 1.1 billion emails contain malware or phishing hooks. And, this is an email channel only. There are several reasons for this growth:
- There are too many vulnerabilities;
- It is cheap and easy to organize an attack, while the potential gains are huge;
- There is too little possibility for a criminal to be caught.
The irony of fate, no organization can avoid cyber risk. Therefore, risk management became a crucial activity for ensuring an appropriate level of data protection.
Risk Management and Cybersecurity
Organizations and businesses are urged to invest more into their security systems to increase protection layers, educate personnel, and backup their critical data. Many companies are only on the way to building their security system. In all cases, no one can feel 100 percent protected.
There are always multiple cyber threats looming out there. We point out that the associated risks will always be imminent, no matter how strong your protection may seem now. It is the matter of IF, it is the matter of WHEN an accident happens and how ready we are to it.
Managing risks enables you to timely address the threats and mitigate damages when a bad event happens.
Risk Management Strategies
A proper risk management strategy supposes a well-aligned holistic approach to all aspects of the risk management process including risk identification, analysis, and evaluation.
Thus, this process is based on regular updating and re-assessing risks for the organization. It does not depend on organization type or size. A single strategy can be applied equally to a big high-profile company or to a small team or project. The same way it can be integrated with a complex enterprise strategy.
The existing uncertainties and constantly emerging new threats leave no space for staying security naïve. By regularly identifying risks and vulnerabilities, an organization increases its general awareness and prepares to act in any worst-case scenario.
Some organizations choose to follow a limited risk management strategy instead of recommended a full-fledged approach.
Examples of Limited Risk Management Strategies

Risk Assessment
Cyber risk is a possibility of any adverse event that may have a negative impact on the organization’s assets. For instance, sensitive data theft, infrastructure, and systems failure, financial or reputational damage, business operation disruption, and so on.
The process of cyber risk assessment includes three phases: risk identification, analysis, and evaluation according to international Information Security standards and practices. It covers not only vulnerabilities of an organization’s IT infrastructure, but also those of every constituent part of the entire organization: people and their connections, business continuity, systems, and processes.
Cyber risk assessment is a primary stage of cyber risk management. By prioritizing the identified risks according to their severity and occurrence probability, cyber risk management implements controls and safeguards to minimize the potential negative impact.
Why Cyber Risk Assessment is Important?
Without prior assessing the potential cyber risks, an organization cannot ensure that security activities and implemented controls are properly aligned and serve to their purpose.
Underestimating or overestimating risks are both harmful to the organization exhausting the resources and wasting finance. It does not have much sense to establish heavy measures against the events, which are unlikely to happen. However, overlooking certain risks can be disastrous.
Cyber risk assessment is not only a best practice. It is a requirement under the modernized legislation and standards. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), as well as other mandatory data protection frameworks, make a specific point upon risk assessment procedure providing detailed guidance on it.
What are Constituents to Cyber Risk Management?
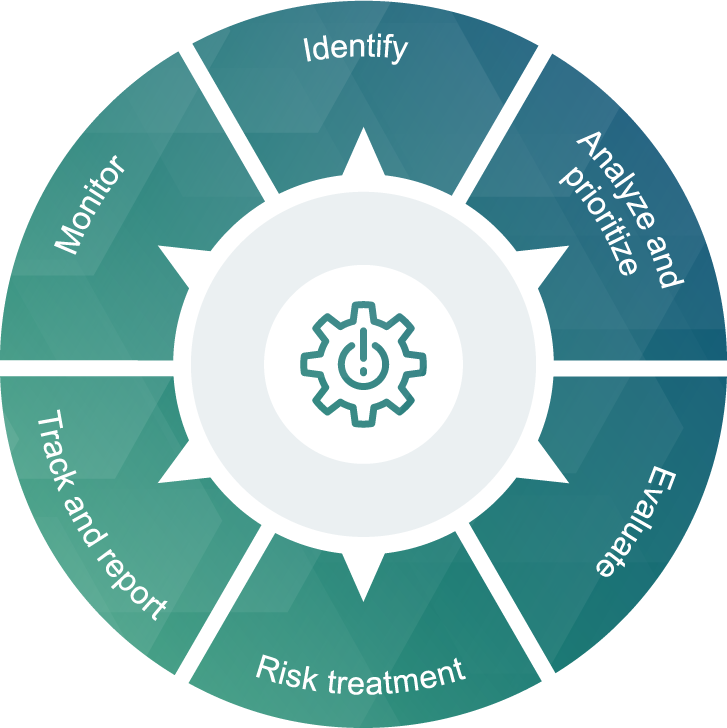
Cyber risk management process starts with identifying all information areas and assets that have the potential to be affected by a cyber-attack or fall victim of any malevolent actor. These are information systems, hardware, data, intellectual property, user software, applications, and the whole environment including employees. Then for each component in the list, individual risks are identified, analyzed, and prioritized as per potential impact and probability.
The next stage is performing an evaluation of each individual cyber risk with establishing controls and action plans for their treatment.
You can see the full cycle of the cyber risk management process in the diagram. It is extremely significant for the organization to monitor continuously its risk environment. It enables timely tracking changes, if any, and updating the risk treatment controls.
What does ISO 27001 Tell about Cyber Risk Management?
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for building robust Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). ISMS represents risk-based methods to manage an organization’s security risks with regard to people, processes, and systems.
In Clause 6.1.2, the ISO 27001 document also lists requirements to organizations with regard to the risk management process:
- Establishing and maintaining accurate information security risk criteria.
- Ensuring that the risk management process provides “consistent, valid and comparable results”.
- Identifying all information confidentiality, integrity, and availability risks “within the scope of the information security management system”, as well as identifying the owners of those risks.
- Regular analyzing and evaluating information security risks in accordance with the prior established criteria.
The organizations also must ensure that the information and related documentation about the risk assessments is properly maintained and updated in compliance with the requirements of the standard.
The ISO 27001 standard contains detailed instructions on the risk management process and its place in the entire Information Security Management System.
Modern Drivers of Cyber Risk Management
In the Digital Age, Cyber Risk Management turns into independent discipline. Hence, its growing importance for the organizations, which are increasingly relying on technologies and digital processes.
Now we are witnessing a few definite world trends pushing the cyber risk management to a new level:
- Increasing losses: Despite the growing security investments globally, organizations and businesses continue falling victims of cybercriminals. The annual financial loss from fraud and cyber-attacks keeps skyrocketing all over the world.
- Minimum-security level: Most of the organization pursue compliance requirements only, which are critical but not sufficient to provide organizations with an appropriate level of protection from current cyber threats. The compliance-centric approach proves to be inefficient in modern conditions.
- Growing connectivity and associated dependencies: Growing interdependencies of Information Technologies like AI, IoT, physical security devices, etc. critically require establishing a risk-based approach to governance and management before facing catastrophic consequences.
- Demand for risk awareness: All levels of personnel starting from Director Boards, C-level executives, and management teams now must be constantly aware of their organization’s cyber risks and understand the basics of information security initiatives.
- Incongruous Methods: Currently most organizations are not ready for risk-based cybersecurity governance and management. They have no established common risk management techniques to quantify and manage cyber risks across all their organization’s structure.
Risk Management Tools and Solutions
To finalize this brief overview we would like to draw your attention to the idea of risk management tools and solutions. Risk management software can dramatically improve the efficiency of your security activities.
The Infopulse Standards Compliance Manager (SCM) is designed as a unified platform for Governance, Risk, and Compliance Management (GRC) altogether.
Find out the detailed info on our webpages about the SCM features and benefits or request a live demo.
Try Compliance Aspekte For Free
Book a 1-2-1 Live Demo and Obtain a 3-months Non-binding Trial
