Risk Matrix: A Guide to Risk Assessment with Examples
With over 10 years of experience in compliance and risk management, Compliance Aspekte presents a detailed guide on risk matrices. A risk matrix can be vital in assessing risks and helping organizations achieve their objectives. In this article, we will consider the following questions:
- What is a risk?
- What is a risk matrix?
- The main types of risk matrices
- How to use a risk matrix?
- The main advantages of the risk matrix
- The role of risk matrix in compliance management
- How Compliance Aspekte can help your organization with risk management.
What is a Risk?
Risk in the business context refers to the potential for adverse events or conditions that could negatively impact an organization’s objectives, operations, or financial performance. It encompasses a wide range of potential threats, including market fluctuations, regulatory changes, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
Nowadays, organizations of all sizes and sectors are exposed to a multitude of risks. Effective risk management has become a critical component of strategic planning and operational execution. It involves the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to ensure business continuity and sustainable growth.
By implementing robust risk management practices, companies can not only safeguard their assets and stakeholder interests but also capitalize on opportunities that arise from well-managed risk-taking. This proactive approach enables businesses to navigate uncertainties with greater confidence and resilience, ultimately driving long-term value creation and competitive advantage.
The main types of risks
Risks might be classified into the following categories:
- Strategic risks are risks that affect the long-term goals and objectives of an organization. Examples of such risks are market dynamics, regulatory changes, technological disruption, reputation risks, economic shifts and others.
- Operational risks are weaknesses in processes or procedures, such as equipment failures, supply chain disruptions, human error, system failures and others.
- Financial risk refers to all situations that result in a loss of profit. These include market fluctuations, legal issues, and competition.
- Technical risk encompasses all aspects of company technology, such as security flaws, power and internet failures, and property damage.
- External risks are certain risks that are beyond control. Floods, fires, natural disasters, and pandemics are some examples of these.
Depending on the industry, the company may need to evaluate other risk categories. For example, if it operates with government clients, it may have to address legal concerns. If it offers a physical product, there might be production risks.
What is a Risk Matrix?
A risk matrix is a powerful visual tool that helps businesses identify, assess, and prioritize potential threats. The risk matrix shows the probability of occurrence of various issues that could affect the organization. This simple yet effective grid shows risks based on two key factors: how likely they are to happen and how much damage they could cause, if they do.
Typically, a risk matrix is set up as a table with 3×3, 4×4, or 5×5 cells. The horizontal axis shows the probability of a risk occurring (from low to high), while the vertical axis represents the potential impact (from minor to severe). By placing each identified risk on this grid, you can quickly see which ones need your immediate attention and which are less pressing.
The main benefit of a risk matrix lies in its simplicity and practicality. It helps categorize risks into different zones, often using color coding. Red might indicate high-risk areas that need urgent action, yellow for moderate risks that require careful monitoring, and green for low-risk items that can keep an eye on but aren’t immediate concerns.
Many businesses combine the risk matrix with the ALARP principle – “As Low As Reasonably Practicable.” This approach helps decide how to handle each risk. Some risks might be unacceptable, and immediate action is needed to reduce them. Others fall into the ALARP zone, where the risk should be reduced as much as possible without breaking the bank. The rest might just need monitoring.
By creating a risk matrix and using it, organizations can make smarter decisions about where to focus their risk management efforts and resources. It’s a straightforward way to turn complex risk information into clear, actionable insights for your business.
Compliance Aspekte is a compliance management tool that has a risk management module. It helps organizations identify, assess, and manage risks more effectively. It automates the process of identifying threats, provides customizable tools to evaluate risks, and uses AI to suggest tasks to address issues.
By integrating risk management with overall compliance efforts, Compliance Aspekte not only boosts the organization’s security but also makes it easier to meet the requirements of various standards.
6 Steps to Understand a Risk Matrix
To use the risk matrix effectively, follow the next steps:
Step 1. Look at the axes
A risk matrix typically has two axes. The vertical axis represents the likelihood or probability of a risk occurrence, while the horizontal axis represents the potential impact or severity of the risk.
Step 2. Identify the risk level zones
The matrix is usually divided into different zones, each with a different level of risk. These zones may be color-coded or marked with labels such as low, medium, high, or critical. The risk zones indicate the level of risk associated with each combination of likelihood and impact.
Step 3. Analyze the risk ratings
Each risk identified in the matrix will be rated according to its likelihood and impact. The risk rating is determined by the intersection of the likelihood and impact scores on the matrix. The risk rating can be expressed as a numerical value or a color-coded score, depending on the matrix used.
Step 4. Interpret the risk rating
Once the risk rating is determined, interpret it in the context of your organization’s risk tolerance. A high-risk rating may indicate that immediate action is needed to mitigate the risk, while a low-risk rating may not require immediate action.
Step 5. Prioritize risks
Use the risk matrix to prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact ratings. Focus on the high-risk areas first and allocate resources accordingly.
Step 6. Review and update
Finally, it’s important to regularly review and update the risk matrix to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. As new risks emerge or the likelihood and impact of existing risks change, adjust the matrix accordingly.
How to Use a Risk Matrix?
A risk matrix is a valuable tool for assessing and managing risks in a formal and systematic manner. To use it effectively, follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify the risks
The first step in using a risk matrix is to identify all potential dangers that the organization may encounter. These dangers might be characterized as internal or external. Internal risks may include financial mismanagement, human mistakes, and supply chain interruptions, whereas external risks might include natural disasters, political instability, or regulatory changes. Fill in the risk matrix with all identified risks.
Step 2: Assess the risks
After identifying the risks, the following stage is to evaluate them. This entails assessing the possibility of each risk occurring and the possible impact it may have on the organization. A risk matrix divides hazards into three categories: high, medium, and low, depending on their likelihood and effect. Create the risk matrix and use it to map each danger and calculate its severity.
Step 3: Prioritize the risks
After you’ve examined the risks, rank them according to their possible impact on the company. Prioritize the highest-risk zones and spend resources appropriately. This might include creating specific strategies for minimizing areas with elevated risks or creating contingency plans for dealing with accidents that do occur.
Step 4: Develop a risk management plan
Create a risk management plan based on your risk assessment and prioritizing results. This strategy should include specific tactics for limiting risks and dealing with occurrences. It should also define clear roles and responsibilities for all participants in the risk management process.
Step 5: Monitor and review
Regularly monitor the identified risks and assess the effectiveness of your risk management strategy. This will allow you to recognize new risks that arise over time and change your strategies accordingly. Also, based on your analyses, do not forget to conduct regular risk matrix maintenance.
Following these steps will allow to create a risk matrix and utilize it to efficiently discover, analyze, prioritize, and manage risks in your company. Remember that risk management is a continual process that needs constant monitoring and assessment to ensure that your business is ready to deal with any potential risks that occur.
The main types of risk matrices
Qualitative Risk Matrix
The qualitative risk assessment matrix is a risk matrix example that uses qualitative analysis of the likelihood and consequences of risks. For instance, when the 4×4 risk matrix is used, the probability and potential damage of each accident scenario are evaluated on straightforward scales, such as low, medium, high, and very high on the probability axis, and rare, medium, often, and very often on the potential damage.
Based on probability and potential damage ratings, we can calculate the risk for each scenario. Thus, with the 4×4 risk matrix, we’ll have twelve pairs of risk indicators:
- Low x Rare
- Medium x Medium
- High x Often
- Very High x Very Often
- Medium x Rare
- Medium x Medium
- Medium x Often
- Medium x Very High
- High x Rare
- High x Medium
- High x Often
- High x Very Often
- Very High x Rare
- Very High x Medium
- Very High x High
- Very High x Very High.
The Low x Rare pair has the lowest risk, while the Very High x Very High pair has the highest risk. Some regions are directly comparable, while others are not. This makes interpreting the intermediate areas more challenging.
Quantitative Risk Matrix
Simply speaking, a quantitative risk matrix is based on evidence-based quantitative risk analysis. In such a matrix, risks are assigned a numerical value based on quantitative data. It means that the potential damage scale can be turned into a numerical scale that allows for quantitative analysis, thus allowing the calculation of relative risks for all matrix areas.
The Role of Risk Matrix in Compliance Management
Risk analysis matrices are essential in compliance management, particularly for information security and data protection.
In information security and data protection, risk matrices are used to detect, analyze, and prioritize possible threats to an organization’s information assets. Sensitive data, such as personal or secret corporate information, can be included in information assets, along with IT systems, networks, and other infrastructure.
Using a risk matrix, an organization can categorize potential risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. This helps organizations prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively to mitigate the most significant threats. For example, a risk matrix may help an organization determine whether a particular security control, such as encryption or access controls, is necessary for a given data asset.
Risk matrices are especially important in showing compliance with information security and data protection standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Identifying and mitigating possible risks allows businesses to show to authorities and auditors that they have taken sufficient actions to secure sensitive data and comply with applicable requirements.
In addition to compliance management, risk matrices may be utilized for continuous risk management and incident response. Organizations may remain on top of new threats by analyzing and updating the risk matrix on a regular basis and adjusting their security posture accordingly. In the case of a security incident or data breach, a well-organized risk matrix may assist businesses in immediately assessing the incident’s effect and determining the best response.
Risk matrices in the Compliance Aspekte GRC tool
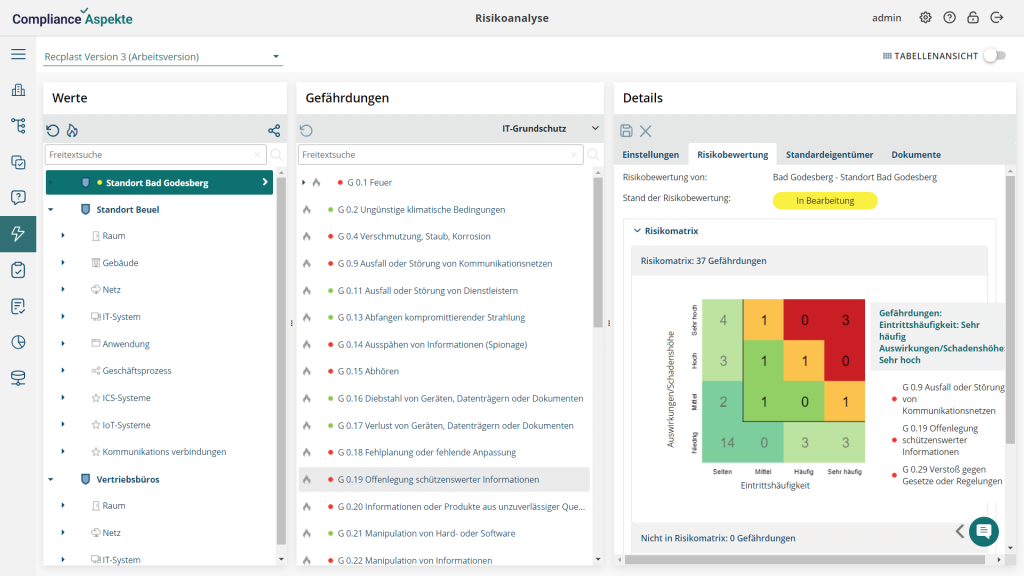
Compliance Aspekte is a GRC tool with a risk management module that assists organizations in identifying, assessing, and mitigating compliance-related risks. The capability to create and use risk matrixes is a significant component of Compliance Aspekte’s risk management module.
The risk matrix in Compliance Aspekte is customizable, allowing organizations to define their own likelihood and impact criteria and weightings and to tailor the matrix to their specific needs and requirements.
The main features of the Compliance Aspekte risk management module are:
- Automated risk allocation: Automatically assigns relevant threats to assets based on predefined criteria, ensuring consistent risk management.
- Risk qualification: Facilitates the assessment of risks by evaluating their probability and potential impact, aiding in prioritization.
- Customizable risk acceptance: Allows for flexible configuration of automatic risk acceptance rules, streamlining decision-making.
- Task integration: Enables the creation of tasks for risk mitigation directly within the module, enhancing accountability and follow-up.
- Continuous monitoring: Provides ongoing tracking of risk status and mitigation progress, allowing for real-time adjustments.
- Comprehensive reporting: Generates detailed reports on risk assessments and management activities, supporting compliance and audit requirements.
- Multi-standard support: Manages risks across multiple standards, ensuring a unified approach to risk management.
The tool also has comprehensive reporting and monitoring capabilities, which enables companies to create customized reports and assess the performance of their risk management activities. Compliance Aspekte software offers several reporting options:
- risk heat maps
- trend analysis reports
- risk matrix reports.
Overall, the Compliance Aspekte tool makes it easier to manage compliance issues. By offering a customizable and flexible approach to risk assessment and prioritization, as well as advanced reporting and monitoring capabilities, the tool enables organizations to effectively identify and mitigate compliance risks while remaining in compliance with applicable regulations and standards.
If your company needs assistance with creating a risk matrix, contact our team. We will be glad to help you and show how our GRC software can improve risk management in your organization.
Try Compliance Aspekte For Free
Book a 1-2-1 Live Demo and Obtain a 3-months Non-binding Trial
