(archive)
How to Check If You Align with the Data Privacy Law: A GDPR Compliance Checklist

Challenge of GDPR Today
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has standardized data protection across all 28 EU countries and imposed stringent new rules on processing and controlling personal user data. All websites collecting data from EU residents are obliged to align with GDPR compliance requirements. If they don’t, they may be fined up to 4% global turnover (or EUR 20 million). So, if people from the European Union frequently visit your website, it pays to be prepared.
What Is GDPR Compliance
Being GDPR compliant means executing all the regulations and subscriptions issued by the General Data Protection Regulation that apply to your organization.
You are eligible for GDPR if:
- Your company processes any data from any data subject who is an EU citizen;
- You expect customers (or visitors to your website) from Europe;
- There is even a small possibility that you may collect data from an EU citizen;
- Any of your third-party vendors collect information on your behalf of you in Europe.
How to Check If You’re GDPR Compliant: Three Basic Steps
Here’s a short GDPR compliance checklist for US companies and those located in the EU on how to become GDPR compliant.
The Law-related Part
Info audit: What data do you process
Organizations must keep an up-to-date and detailed list of their processing activities. This list should include answers to the following questions:
- For which purposes do you process data,
- What kind of data do you process,
- Who has access to processed data in your organization,
- What third parties have access to this data and where they are located,
- What are you doing to protect the data (e.g., encryption),
- When do you plan to erase collected data (if possible).
The regulators may request to submit this list to them at any time.
What’s your legal justification for your data processing activities
According to GDPR, processing data is illegal unless you justify it by one of six conditions (Article 6, Articles 7-11).
- Consent
- The necessity for the performance of a contract
- Compliance with a legal obligation
- Protection of vital interests of people
- Task performance of public interest or official authority
- Legitimate interests.
After you choose a lawful basis for processing, you should document your rationale.
How transparent is your privacy policy
Setting up a clear privacy and cookie policy is one of the primary GDPR compliance requirements. Here’s what your privacy policy should include: informing people that their data is being collected; the purpose of gathering data; information processing activities; information about people who have access to collected data; measures to be taken to keep the collected data safe.
Provide your privacy policy to people before or at the time you collect their data. Make it easily accessible on your website and use simple language.
The Information Security Part
Data protection by design and by default
To be GDPR compliant, you must incorporate strict data protection concepts into the core of your organization, following the principles of “data protection by design and by default, ” outlined in Articles 5 and 25. Take all technical and organizational measures to ensure the safety of the data you collect and process.
Pseudonymization and encryption
To keep the data safe, the GDPR requires companies to use encryption or pseudonymization whenever possible (Article 32).
Internal security policy
Set up strong operational security. Your internal security policy must ensure that your employees and team members have sufficient knowledge about data security. Besides, it should include guidance about passwords, VPNs, two-factor authentication, email security, and device encryption. Make sure that personnel with access to personal data receives extra training.
Data protection impact analysis (DPIA)
DPIA helps you understand how your service or service could threaten your customers’ data and how to mitigate those risks. You are obliged to conduct DPIA whenever you plan to use collected data to pose a high risk to the rights and freedoms of data owners.
72 hours notification deadline for data breaches
In case of a data breach and personal data exposure, you have 72 hours to notify the regulator in your jurisdiction about the incident. Besides, you are obliged to inform the affected people about the risks the breach imposes on them.
Accountability
Assign a DPO or a responsible contact person
The Data Protection Officer is a person who monitors GDPR compliance, advises on data protection impact assessments, performs data protection risk analysis, and cooperates with data protection authorities. If your organization operates outside of the EU, you must appoint a representative in that country to contact on your behalf with the regulators.
Sign a data processing contract with your vendors
If any third-party vendors manage any information about your data subjects (e.g., email services, analytics software, or cloud servers), they must comply with the GDPR. Typically, their websites must contain a data processing agreement.
GDPR Cheat Sheet
These simple things will help you to implement the data privacy law in your organization successfully
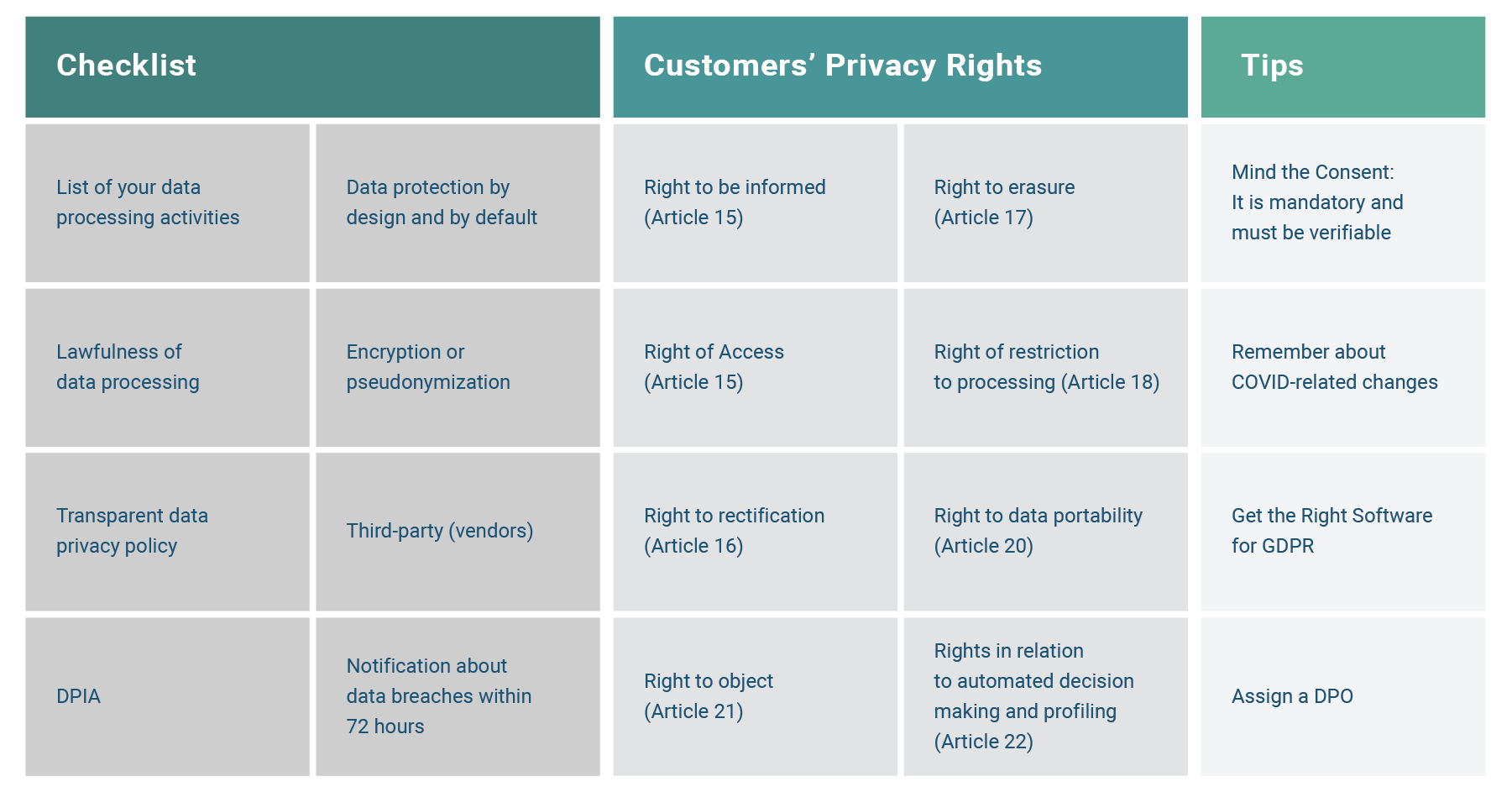
Remember Your Customers’ Privacy Rights
There are several privacy rights that GDPR designates and strictly controls. You have one month to handle the right-related request in most of them, and in each case, you must try to verify the identity of the person making the request.
The right to be informed. People have the right to see what personal data you have about them and how you’re using it.
The right of access. People have a right to know how long you plan to store their information and why you will keep it. A copy of this document must be sent to your data subjects.
The right to rectification. Keep data up to date by setting a data quality process, so your customers can easily view and update their personal information.
The right to erasure. People have the right to ask you to delete all the personal data you have about them. There are five grounds on which you can deny the request, such as exercising freedom of speech or compliance with a legal obligation.
The right to restrict processing. People can request to restrict or stop processing their data if there’s some dispute about the lawfulness or accuracy. Notify data subjects before you start processing their data again.
The right to data portability. You should be able to send people’s data that would be easy to read, e.g., a document or a spreadsheet either to them or to a third party they define.
The right to object. If you’re processing data for direct marketing, people can request to stop processing it immediately.
Rights concerning automated decision-making and profiling. If your organization deploys automated processes for decision-making, you’ll need to set up a procedure to ensure you are protecting persons’ rights, freedoms, and legitimate interests. It should be easy for data subjects to make decisions and request human intervention.
What You Need to Know About the Consent in GDPR
Consent is mandatory and must be verifiable. The GDPR states that the consent a user makes must be a positive opt-in, specific, freely given, and unambiguous. Consent should stand separately from other terms and conditions, and you must inform people how they can withdraw their consent.
GDPR and COVID-19: What Has Changed?
The European Data Protection Board has adopted new guidelines on personal data used to track the Covid-19 outbreak. One of them is guidelines on geolocation and other tracking tools. They allow controllers to use location data and contact tracing tools in two specific cases:
- For modeling the spread of the virus for evaluation of the overall effectiveness of quarantine measures;
- For notification of people who are likely to have contacted virus carriers.
Get the Right Software for GDPR
Manual data management in compliance has long gone into the past – most companies choose to implement data privacy laws and other regulations and standards through automated compliance solutions. These tools allow operators to gain a holistic approach to compliance and eventually save much time. Сompliance Aspekte is the solution that supports the establishment and operation of a robust data protection management system (DPMS) in your organization. It enables you to meet the requirements of GDPR and other relevant regulations.
With the help of the software, you will handle risk management, tracking measures, reporting, and evaluations. Besides, the process of collection of possible incidents will be gathered and processed.
Final Word
The maintenance of GDPR is a challenge for many organizations. For your GDPR compliance to be on the top, it is together with automated compliance software to control assets, generate quick reports, provide instant access to all the data, etc.
If you are eligible for any other laws or regulations, the GRC solution will enable you to manage multiple standards under one umbrella. You will gain significant benefits and maintain a holistic approach regarding your compliance strategies.
Read more8 Pain Points of the Compliance Officer

The compliance process has many pitfalls in a practical plane. What they are and how they can be successfully resolved with automation solutions, read in our article Dealing with the Best Compliance Management Solutions.
This time we decided to focus on the compliance challenges from the perspective of the Compliance Officer’s duty. We picked eight of them, which seem to us most acute. In this material, we will not speak of what a compliance officer is, what a compliance officer does, and things like compliance officer education and compliance officer certification.
First Pain Point of Compliance Officer: Pushing through the Implementation Stage
Giving a kick-start is the hardest phase. Without the full support of the company’s leadership, you will not go too far. Implementation of the standard is not just a bundle of documentation. It is about building new processes, which were not in place before.
The leadership has to prioritize compliance-related issues and transfer them to middle managers. The middle managers move it down further. It is getting harder with each level. Much is lost on the way. Compliance is not a thing you can push through, from top to bottom, as an imperative.
Pain Point #2. Compliance Officer’s Individual Risks
It very much differs from country to country. In general, the recent narrative of the regulators contains the idea of holding employees liable for corporate wrongdoing or misconduct. Due to their highly responsible positions, the Compliance Officers feel like walking on fire.
This new shift in attitude makes a prominent milestone. There have been precedents when Compliance Officers were heavily sanctioned for failing to control the organization’s compliance posture.
It is not only about keeping the organization safe. The existing governance structure and prevailing attitudes may be a major obstacle to getting things properly done. The reputation of Compliance Officers is at stake. The looming risk of becoming a scapegoat and being fired adds a little comfort to their seats.
Paint Point #3. Growing Workload and Limited Resources
As someone wittily mentioned, we need more and more people to do even less work. The downside of this trend reflects in budgeting. Instead of adding staff to meet their compliance needs, some organizations demand Compliance Officers to “move hills” with less labor force.
These organizations do not fully realize the balance between compliance costs and non-compliance consequences. Getting funds for keeping the compliance department up and running becomes a daily struggle. Compliance seems the least priority if things go all right. When a bad accident occurs, it entirely becomes Compliance Officer’s fault. Nobody cares how hard he tried to push the burning issues through the desks and boardrooms.
Pain Point #4. Increased Penalties and Fines
In the age of massive digitalization and further expansion of connected devices, the exposure of the entire society to cyber threats critically grows. This is one of the reasons regulators increase their requirements for security.
Hefty penalties and fines for non-compliance change the landscape of the IT industry. Some time ago, penalties were an affordable price for doing business. Now, the fines and reputational risks outweigh the cost of implementing well-built compliance systems.
Improving compliance takes a lot of effort and translates into a higher cost. Compliance Officers have to fight the resistant opinions in the boardroom trying to convince the leadership in the necessity of such investment. Often to no avail. As a result, if a penalty occurs, they are first to blame.
Pain point #5. Lack of Compliance Culture
Compliance Officers have trouble delivering bad news to the board of directors. When you have 15 minutes twice a year to report, raising tough issues requires courage. Everyone wants to shine. If the painful part is kept reserved, senior staff would think all is fine and there is no need for action.
On the other hand, compliance alerts and initiatives can find no support in company divisions. Without understanding the proper place of compliance in the company, employees tend to ignore it. You cannot inject it into their minds.
Compliance principles should go along the same lines as the Code of Conduct and Ethical Business Practice. Implementing a compliance culture across the entire organization is a long-term process. Before it is in place, Compliance Officers experience additional pressure from underestimation and lack of support.
Pain Point #6. Massive Migration into Social Media and Messengers
We live in the age of unified communications. New means and tools for connecting people are born almost daily. The population promptly adopts instant messaging and social media networks. The traditional phone calls and emails are going in the past.
New regulations require keeping a record of all transactional electronic communications. From a technical point of view, it is not a problem. However, when employees use their own devices for processing the company’s sensitive information, it poses a serious challenge for Compliance Officers. For example, many software development companies practice a Bring-Your-Own-Device (BYOD) policy. The security of proprietary information stored on personal devices is out of control. This situation gets worse when employees handle personal data via their own gadgets. This poses a serious privacy risk. Writing prohibiting policies does not work. Employees often ignore them or openly protest. Supervising everybody’s communications at work is costly. It is also very uncomfortable in terms of corporate climate.
Pain Point #7. Keeping Pace with Current Technology
Handling enormous amounts of data requires advanced technology. The trick is that the most advanced tools on the market fast become a regulatory expectation. With legacy systems, you are not able to catch up with the growing requirements.
Compliance technologies are changing fast. Some engage in artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies. Compliance Officers are not supposed to be technology experts. The integration of new systems is a big concern. Ensuring that all cyber risks are properly addressed with every innovation becomes a heavy task.
Pain Point #8. Ever-changing Regulatory Landscape
We deliberately put this point to the last place on the list. Regulatory change is the most known compliance issue. Keeping track of local regulations takes its due. Business transactions cross borders. This adds another burden onto the Compliance Officer’s shoulders to monitor, know and satisfy regulations of other jurisdictions. This point closely relates to the compliance officer education and their
As an Afterthought
One day, the decision on the implementation of a standard comes out of the boardroom. What to start with?
It is important to outline the exact area and scope of the standard application. A transnational company with branches all over the world has to maintain compliance across many jurisdictions. On the contrary, a small company acting on a local market finds enough to cover a few of its most prominent processes.
In addition to security and privacy compliance, organizations have to comply with industry-specific standards. Transitioning to another industry can be a challenge for the Compliance Officer.
Some of the pain points above are inherent to the organization. For example, underfunding or lack of compliance culture. Regardless of specialization like Safety Compliance Officer, Compliance Officer, or Corporate Compliance Officer, addressing these issues demands from the Compliance Officers much courage, time, and effort.
Contact our security experts for advice. Find out how innovative integrated platforms like Сompliance Aspekte can revolutionize your compliance system.
Read moreEnergy Sector Compliance: Regulatory Outlook

With the globally increasing dominance and effectiveness of technology, innovation in the energy sector is escalating, and the industry needs to keep up with the pace of change. Organizations should be ready to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing environment, successfully deal with any arising issues, and take opportunities to benefit from the innovation in the energy sector. The approach to compliance should become more holistic, enabling companies to resolve upcoming issues and threats in a cost- and time-effective manner.
Main Prognosed Challenges in Energy Sector
With the energy sector growth, the industry faces numerous challenges, depending on the region, business specifics, regulatory, and law environment. They also relate to security and incident response. It is accompanied by changing regulations, e.g., the KRITIS and BSI IT-Grundschutz 2.0 in Germany.
Some of the major problems of energy sector expected in 2021-2022 are as follows:
- Long-lasting effect of the COVID-19 crisis. According to the World Energy Outlook, the Recovery Scenario expects prolonged pandemic consequences. Given the global economy comes back to its pre-crisis state only in 2023, the rates of energy demand growth are the lowest since the 1930s.
- Rapid advancement of Europe’s green policies. They are expected to push on more quickly, posing challenges for many companies to align with. By 2030, companies will have to cut emissions by 55%, which will lead to an increase in renewable energy and energy efficiency targets. New rules will influence the fossil fuels sector, including natural gas, and make future funding of such projects unlikely. Besides, the demand for energy will rise as the Bitcom forecasted that more than 50% of the reduction of emissions will be achieved due to digitalization.
- Growing urge to harden security. Challenges in securing the energy sector and IT security have always been a critical issue and will continue to be the most burning topic the next few years. During the last two decades, nearly 11,500 oil & gas pipeline-related incidents took place. They resulted in approximately 320 fatalities and more than 1,300 injuries, which has led to an estimated $7Bn of direct costs to operators with an average cost per incident of ~$1MM.
- Heavy regulatory pressures for non-compliance. Besides immediate fines and fees, companies are subject to non-financial penalties such as loss of operating license, associated negative reputation with the regulators, potential future partners, and the general public. The list of NIST standards that deal with cloud computing in the energy sector is increasing.
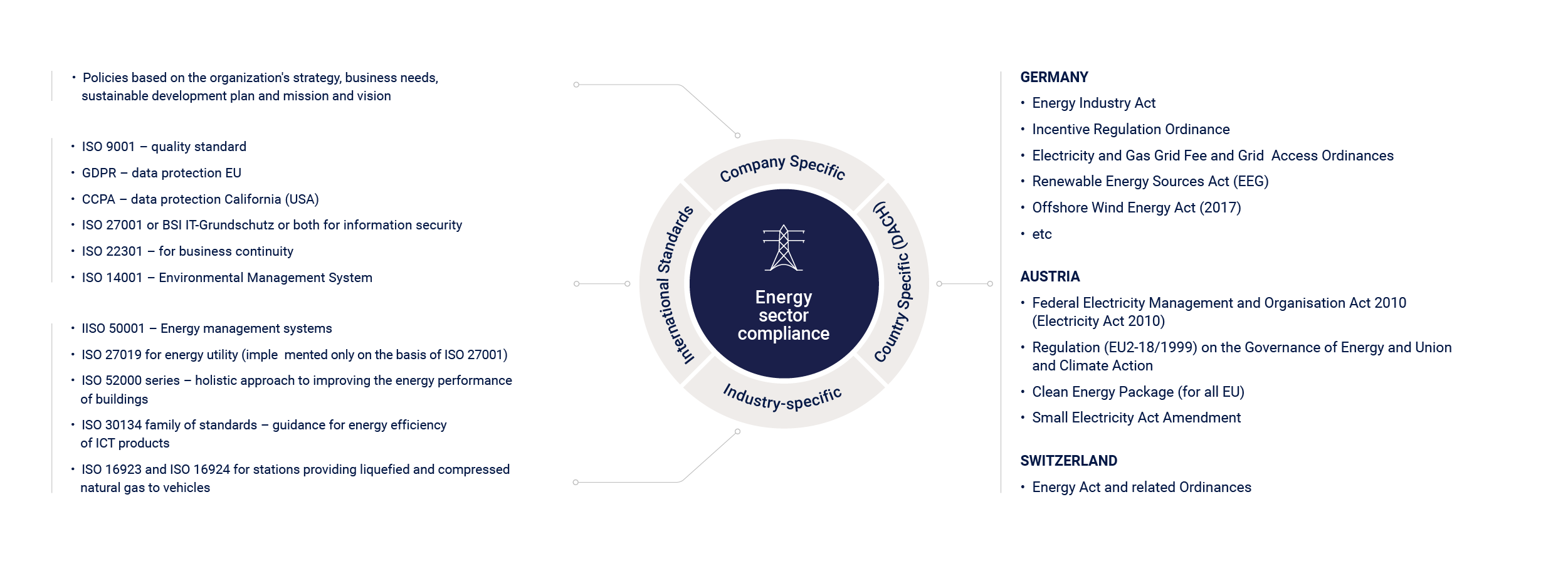
Compliance: Standards Overview for Energy Sector
To maintain market competition and reputation, protect their assets, data, preserve business continuity and environment, boost innovation in the energy sector, organizations need to comply with a list of international regulations obligatory for this sector.
Besides international standards on security, quality, data, and environmental protection, and business continuity, there are industry-specific standards for energy companies to align with, such as ISO 50001 and ISO 27019. If the company deals with renewables, there are more specific applicable regulations, i.e., for solar energy. The energy industry peculiarity is that every country may have very stringent regulations regarding energy management they need to align with. Energy organizations operating in the DACH market have several laws and industry acts to take into consideration.
Company-specific policies depend on the organization’s strategy, business needs, sustainable development plan, mission, and vision. Companies in any country can decide to have additional internal regulations to align with.
Practical Tool-driven Implementation Framework for Energy Companies
To stay afloat and deliver added value to their partners and end customers, companies need to effectively deal with problems of the energy sector, but also follow the major industry trends today.
Organizations in the industry face even more challenges regarding security, data privacy, risk assessment in the energy sector, and experience additional pressures due to a large number of standards and regulations.
Cost-effectiveness requires centralization of activities in avoiding non-compliance fines, reducing the number of incidents, and improving audit response time. Importantly, companies should pay specific attention to improve compliance and reduce significant incidents causing environmental or property damage that have been increasing within the last ten years. Companies can reach centralization and standardization with an innovative holistic approach empowered by a modern GRC solution, such as Infopulse SCM, enabling companies to focus all their effort regarding security, data protection, quality, and environmental management in one place.
Highlights of Infopulse SCM
- Holistic solution including all relevant frameworks like ISO 27019, B3S, C5 Controls and further;
- Monitoring and optimization of compliance in one place and one report;
- Instant access to vital information for internal and external audits;
- Cost reduction, including labor and time costs;
- Avoidance, minimization or reduction of compliance fines;
- Optimization of business and IT processes in the company.
Maintaining Standards for Energy Sector
As regulatory activities are on their way to full or partial digitalization, companies should attempt to advance their compliance. Also, standardizing processes through digitization and automation can bring crucial operating efficiencies and reduce the time and effort needed to complete tasks. This will allow the company leaders to pay more attention to strategic initiatives, proactive management of regulatory risks, boosting risk assessment in energy sector and business continuity. Implementing a tool-driven approach in compliance management for the energy sector can bring significant benefits allowing companies to resolve challenges quickly and align with the international standards and regulations.
Infopulse SCM team is continuously monitoring the market trends and demands and adding new functionality to the software to help companies succeed in their compliance journey.
Read moreHow to Eliminate Challenges When Building a Compliance Strategy? Turnkey solution from wibocon GmbH and Infopulse SCM


As the regulatory environment becomes more demanding, the number of challenges businesses are facing increases continuously. Add unpredictable business landscape and growing non-compliance consequences resulting in security issues, fines, and brand reputation.
Together with our consultancy partner wibocon GmbH, we have held an exclusive workshop where you can learn how to address real-life obstacles when building compliance strategies effectively.
Highlights:
- TOP challenges based on 25 years of experience of our partner wibocon
- The practical solution from a consultancy perspective
- Tool-driven approach to compliance strategy using Infopulse SCM: live demonstration
- Q&A session
Find answers to your compliance pain points during the workshop from our experts:
- Markus Willems, CEO of wibocon GmbH
- Jan Keil, Infopulse SCM
- Andriana Piniak, Infopulse SCM
In case you missed our webinar, all webinar materials are available via the following links:
We are looking forward to welcoming you at our next events and webinars!
Read moreHow to Align with Data Privacy Regulations


The Data Protection Day occurs every January 28 as a reminder about maintaining online privacy for internet users and GDPR compliance for businesses. The tradition dates back to Jan. 28, 1981, when Convention 108 – the first legally binding international treaty dealing with privacy and data protection was signed. The US and Canada started to celebrate it as “National Data Privacy Day” in 2014. This Day is aimed to emphasize the importance of privacy awareness and education effort.
Why Online Privacy Matters More than Ever Today
2020 was the year to change businesses forever. The e-commerce market grew by 18% during the last year, while 75% of buyers and sellers now prefer digital communication to personal offline interactions. As businesses were forced to go online due to pandemics in 2020, it became crucial for online sellers to grasp their online data protection and privacy. More businesses that have switched to e-commerce and deal with personal information face regulatory pressures from data privacy authorities.
Data Privacy in 2022: Things to Consider
- Regulatory and legal activity related to employee privacy will double in the next 12 months, as organizations will have to collect more and more employee data. Companies that fail to take a thoughtful approach to employee data will face an increased flow of employee privacy lawsuits in 2021. Organizations should pay specific attention to privacy by design when processing employee personal data.
- Besides reviewing GDPR-related activities, businesses need to consider industry-specific regulations on data privacy.
- Incorporating “data as a service” solutions will enable organizations that collect, analyze and responsibly share data with third parties to create unprecedented revenue opportunities.
- The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) 2.0 will introduce federal privacy legislation in the US. Organizations need to identify what aspects of CPRA will apply to them and keep their eyes turned toward the national legislation when introduced to adjust their approach.
- To get things settled with data protection, it is crucial to keep fingers at the pulse and include data protection law into your compliance strategy.
What’s Ahead: Experts’ Forecast
“Things changed in 2020; digitalization continued to experience extreme growth. The progress likely will not stop in 2021. As it was crucially important to adapt to new requirements quickly, it will be even more critical this year to scrutinize and analyze business processes and data flows. The question “who receives certain personal data and for what reason?” becomes ever so important, making them compliant to the regulations of GDPR.
Daniel Schreiner, expertree consulting
Together with expertree consulting’s “Data Privacy as a Service” – powered by Infopulse SCM – we can help customers position themselves accordingly, become compliant to new requirements, and adopt recommended actions powered by our tool-driven “Data Privacy as a Service.” And due to the collective intelligence of best practices garnered over time, every customer benefits directly from the experience as well as lessons learned by other customers in our network.”
Conclusion
New regulatory pressures on data privacy require a new approach to its management to keep your data safe and align all the data management processes with relevant regulations. Maintain your data protection smartly with a 365 compliance solution Infopulse SCM that encompasses ROPA and TOMs for GDPR compliance and allows you to manage multiple standards within one tool.
Read moreEffective and easy-to-use IT security management system based on the latest standards and regulations — from planning and establishing the security concept to certification.
